National Academy of Engineering Selects Young MRI Researcher for Prestigious Frontiers of Engineering Symposium
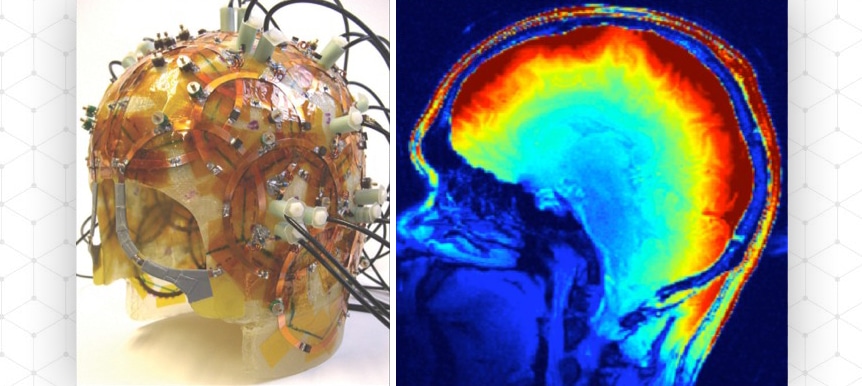
Riccardo Lattanzi will participate in the National Academy of Engineering’s E.U.-U.S. Frontiers of Engineering Symposium, an invitation-only gathering of 60 early-career scientists designed to promote interdisciplinary research collaborations. Lattanzi’s research probes the interaction between the radio frequency electromagnetic fields used in magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and human tissue. He is developing novel noninvasive methods to map the electrical conductivity and permittivity of various tissue types — information that could maximize the diagnostic benefits of MRI.
Lattanzi is an associate professor of electrical and computer engineering at the NYU Tandon School of Engineering and radiology at the NYU Langone School of Medicine. He is also a member of NYU WIRELESS, a multidisciplinary research center focused on developing next-generation wireless technologies.
Lattanzi explained that predicting how and where radiofrequency energy is absorbed and dissipated in the body is a challenge that hampers efforts to improve the sensitivity of modern MRI scanners. “We have to keep these machines on a leash because we are still unable to control their full power,” Lattanzi said, noting that for safety reasons, ultra-high field MRI scanners often operate at power levels below their capacity due to this knowledge gap.
Measuring the electrical properties of tissues would enable MRI engineers to monitor and control radiofrequency energy deposition. In addition, these measurements could also reveal local changes in conductivity that may serve as biomarkers for cancer and other pathologies, and could help improve the accuracy of medical procedures including radio frequency ablation, a technique used to target malignant cells.
During the two-day Frontiers of Engineering conference, which takes place November 16-18 at the University of California, Davis, Lattanzi and his fellow symposium participants will attend poster presentations and discussion sections in four areas: space exploration, next-generation solar cells, neuroengineering, and computational imaging. Lattanzi’s presentation is entitled, “Interaction between Radiofrequency Fields and Biological Tissue in Magnetic Resonance: Challenges and Opportunities.”
In 2015, Lattanzi received the prestigious Faculty Early Career Development Award— also known as the CAREER Award — from the National Science Foundation. He is also the recipient of the I.I. Rabi Young Investigator Award from the International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.

 2026 Open House
2026 Open House 2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit — November 5-7
2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit — November 5-7 Sundeep Rangan & Team Receive NTIA Award
Sundeep Rangan & Team Receive NTIA Award