A New NYUSIM: Moving Toward AI-Enabled Channel Modeling for Future 6G Applications
NYU Wireless P.I.s
Research Overview
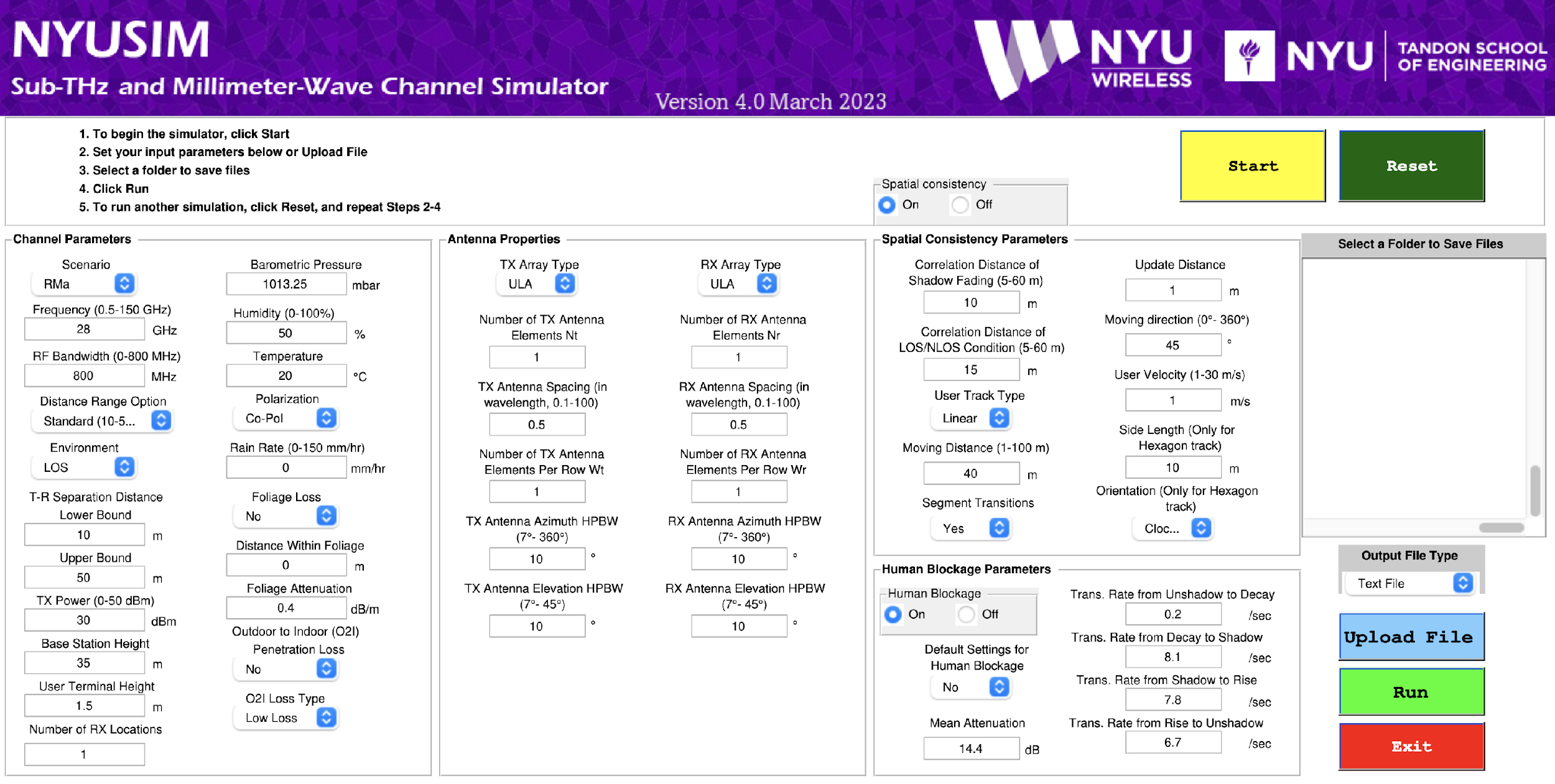
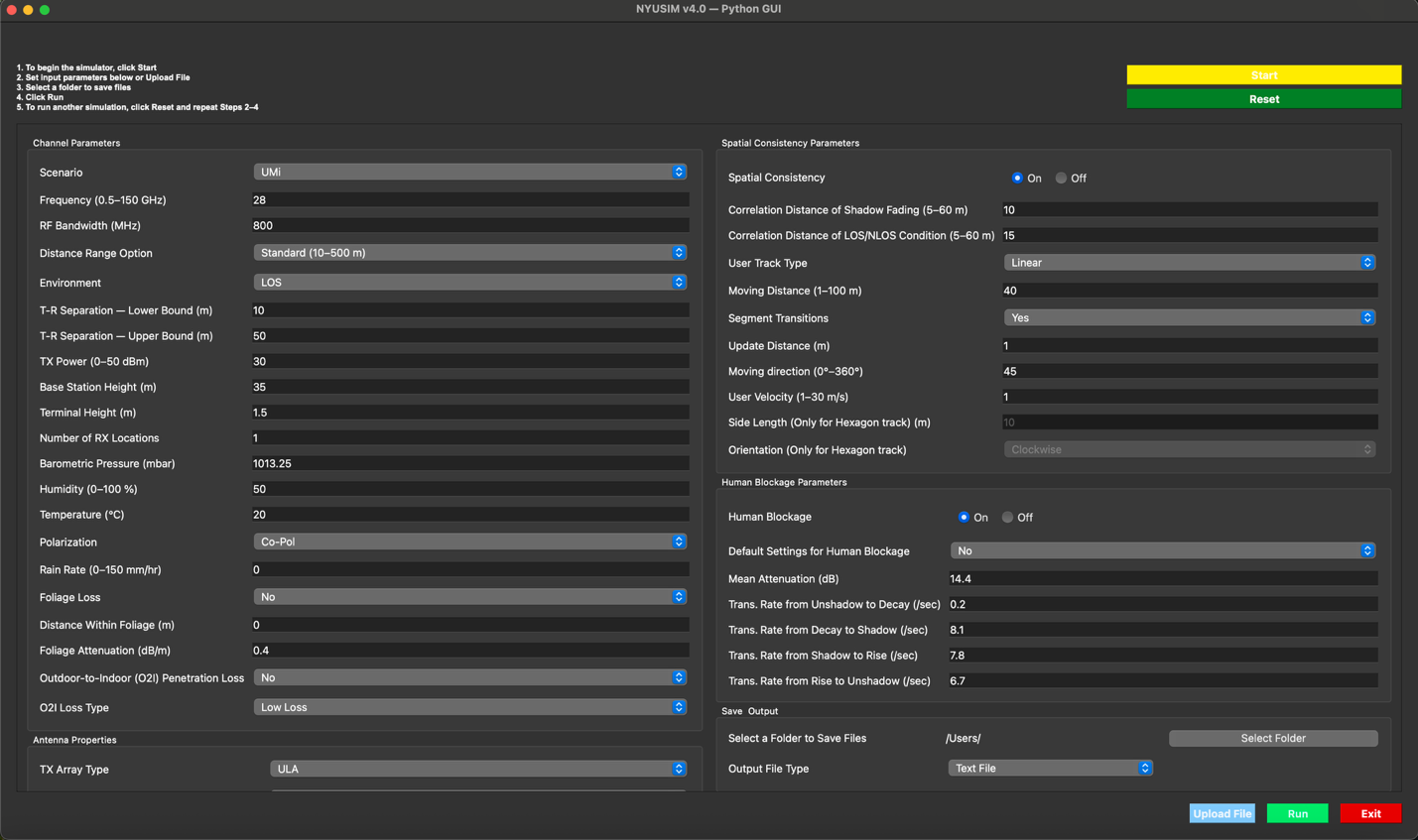
NYUSIM v4.0 is an advanced open-source wireless channel simulator for millimeter-wave (mmWave) and sub-terahertz (sub-THz) frequencies, developed in MATLAB and ns-3, and freely available for academic and industrial research worldwide. NYUSIM v4.0 has now been fully migrated to Python, expanding accessibility and laying the foundation for future AI integration in wireless channel modeling and simulation. The original MATLAB platform has become a global standard for modeling mmWave and sub-THz wireless channels. NYUSIM v4.0 has been downloaded by more than 100,000 users across academia and industry, serving as the statistical foundation for many 3GPP and IEEE modeling discussions.
Conversion of NYUSIM v4.0 from MATLAB to Python
NYUSIM Python is the next step in the evolution of the open-source NYUSIM channel simulator, developed at NYU WIRELESS with support from NYU WIRELESS Industrial Affiliates and the National Science Foundation (NSF). Building upon the MATLAB foundation that has supported thousands of researchers and standardization bodies worldwide, the new Python version brings faster computation and integration with artificial-intelligence (AI) workflows for beyond-5G and 6G wireless research. NYUSIM Python maintains the same measurement-based modeling validated through over a decade of propagation measurements in urban, indoor, factory, and rural environments. It will also include FR3 (7–24 GHz) modeling and statistics. FR3 occupies a critical position bridging sub-6 GHz and mmWave frequencies, offering both extended coverage and high capacity.
Towards AI-Enabled Statistical Channel Modeling and Simulation
As AI and data-driven methods become central to modern wireless design, flexible and scalable simulation tools are essential. The newly developed NYUSIM Python meets this need by reimagining the simulator for today’s research workflows, bringing modern usability while maintaining the same real-world measurement foundation and trusted statistical models that define NYUSIM v4.0. With NYU WIRELESS continually adding new measurement campaigns, NYUSIM Python provides a reliable and transparent interface for generating measurement-based, gold-standard datasets, while enabling seamless integration with modern AI and machine-learning frameworks.
Main features of NYUSIM v4.0:
- Wide Frequency Range: Supports simulations from 0.5-150 GHz.
- Environments and Conditions: Includes UMi, UMa, RMa, InH, and InF scenarios, under both LOS and NLOS.
- Antenna Modeling: NYUSIM Python will support customizable and commercial 3-D antenna patterns.
- Simulation Modes:
Drop-Based Mode: Generates statistically independent channel realizations for user-specified TX-RX separations.
Spatial Consistency Mode: Produces channel responses that evolve smoothly with receiver motion, ensuring spatial consistency.

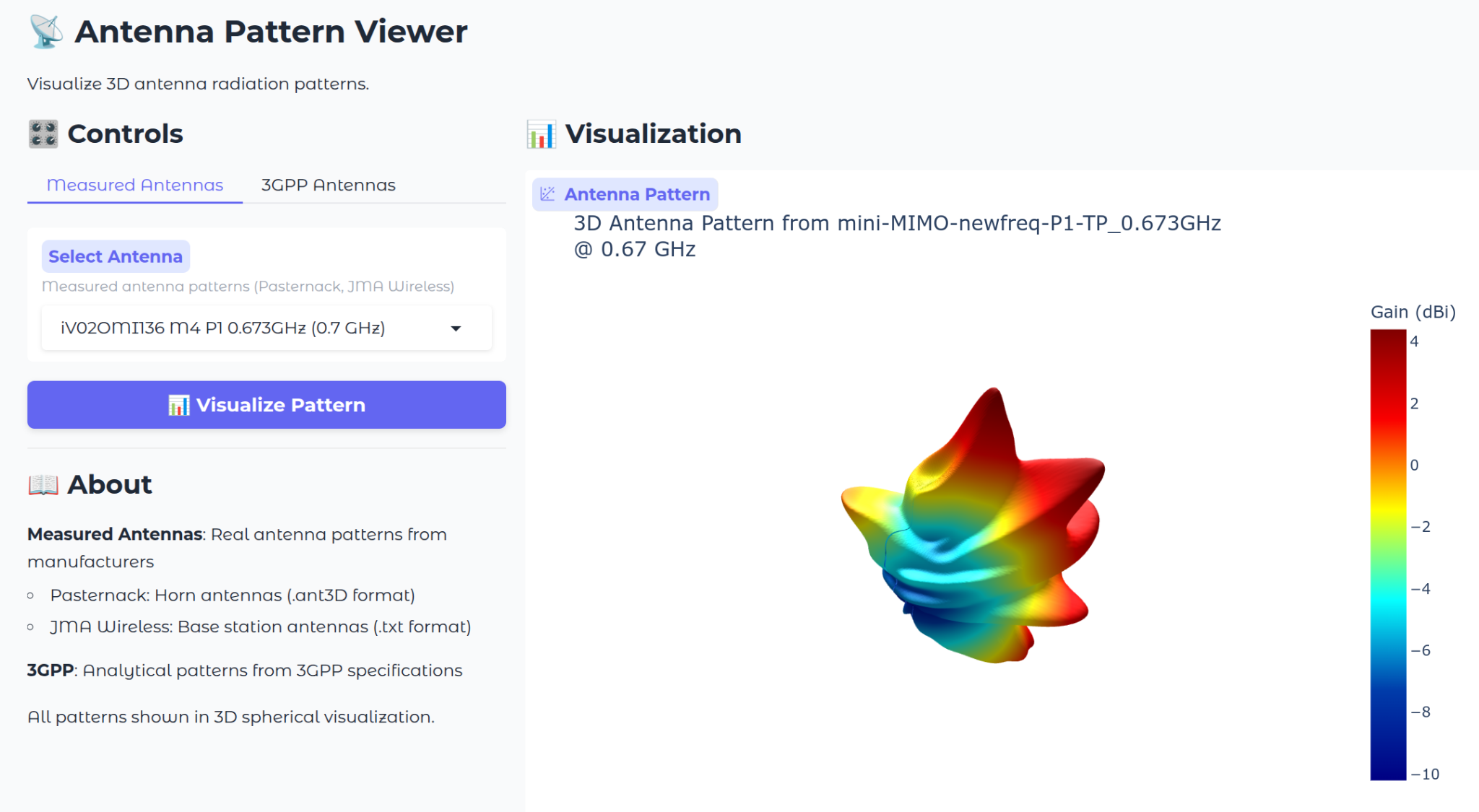
Implementing Customizable and commercial 3D Antenna Patterns in NYUSIM
The Python version of NYUSIM adds a new feature for realistic three-dimensional antenna modeling that allows both measured and commercial radiation patterns to be used directly in spatial channel simulations. Antenna characteristics are stored in a standardized spherical format, referred to as 3Dant, which contains gain, phase, and polarization data across azimuth and elevation. This approach makes it possible to import patterns obtained from electromagnetic solvers or laboratory measurements and to represent beam directivity, sidelobes, and polarization mismatch in the modeled channel response. For each simulated multipath component, NYUSIM interpolates the antenna gain in the direction of departure and arrival, adjusting the received power accordingly.

 2026 Open House
2026 Open House 2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit — November 5-7
2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit — November 5-7 Sundeep Rangan & Team Receive NTIA Award
Sundeep Rangan & Team Receive NTIA Award