5G Connected Intelligent Wearables for People with Blindness and Low-Vision
NYU Wireless P.I.s
Research Overview
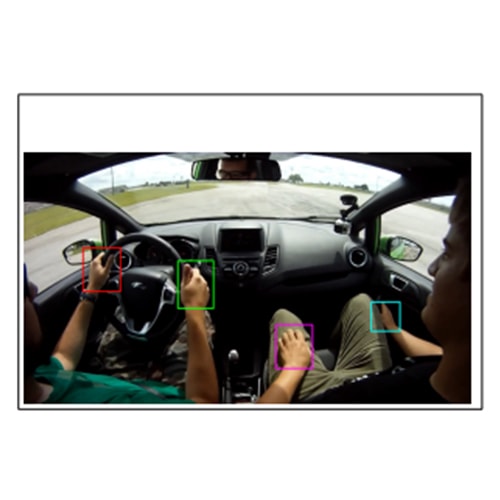
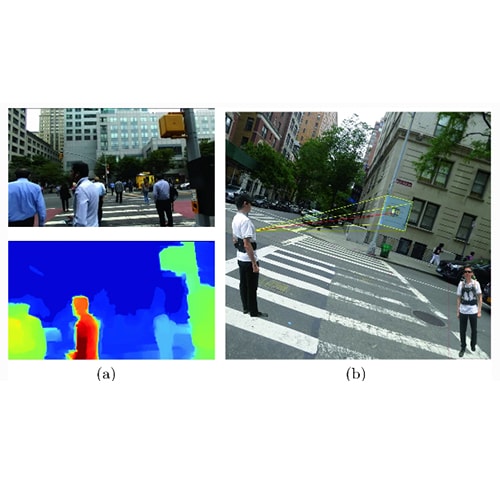
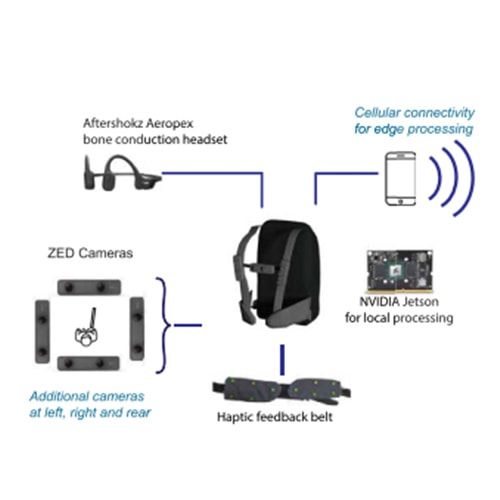
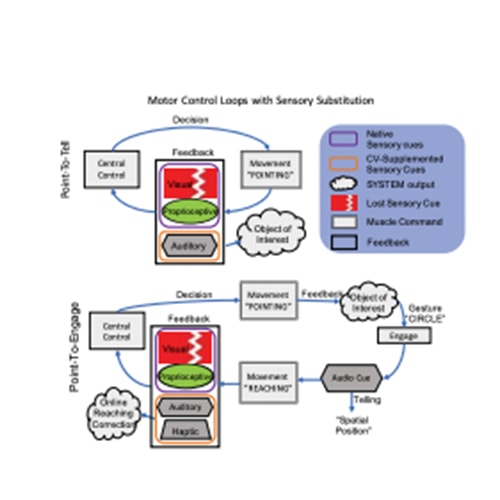
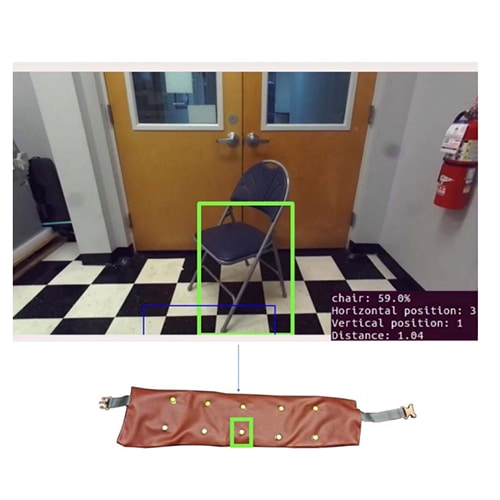
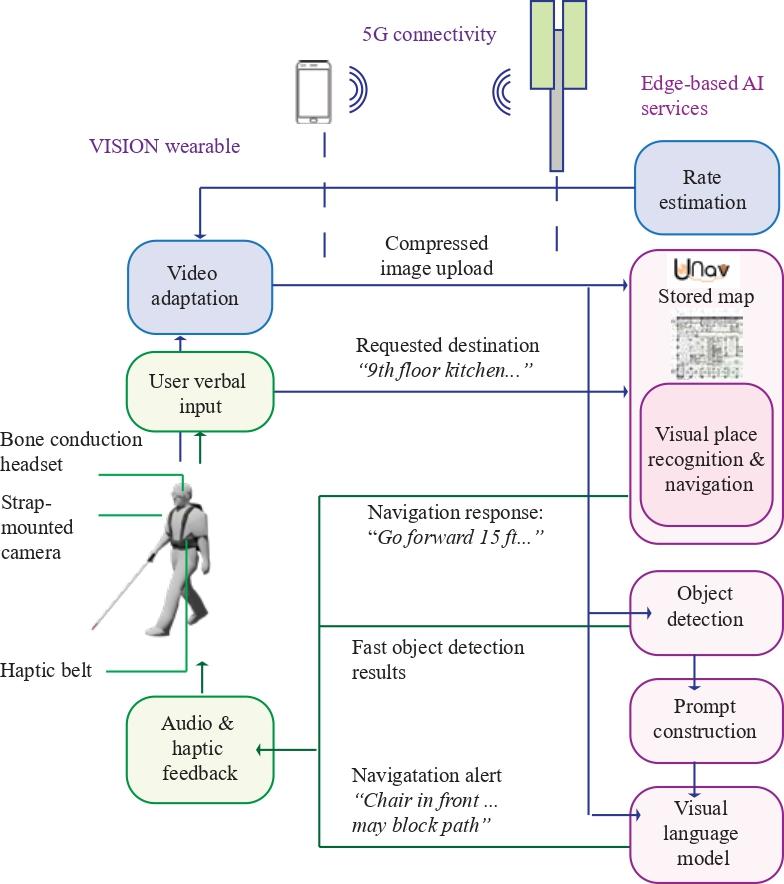
There are 39 million blind and 246 million people with low vision worldwide, according to the World Health Organization. While therapeutic advances are being developed for a handful of conditions, many etiologies result in severe visual disability, and many of these conditions are increasing. Impaired vision constrains mobility, inevitably leading to problems with unemployment and quality of life, both of which limit psychosocial well-being. To address these challenges, we have developed VIS4ION (Visually Impaired Smart Service System for Spatial Intelligence and Onboard Navigation) – a discreet, ergonomic wearable equipped with miniaturized sensors, including cameras, microphones, global navigation satellite system receivers, and inertial measurement units.
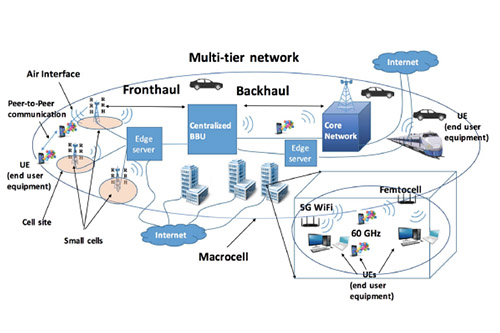
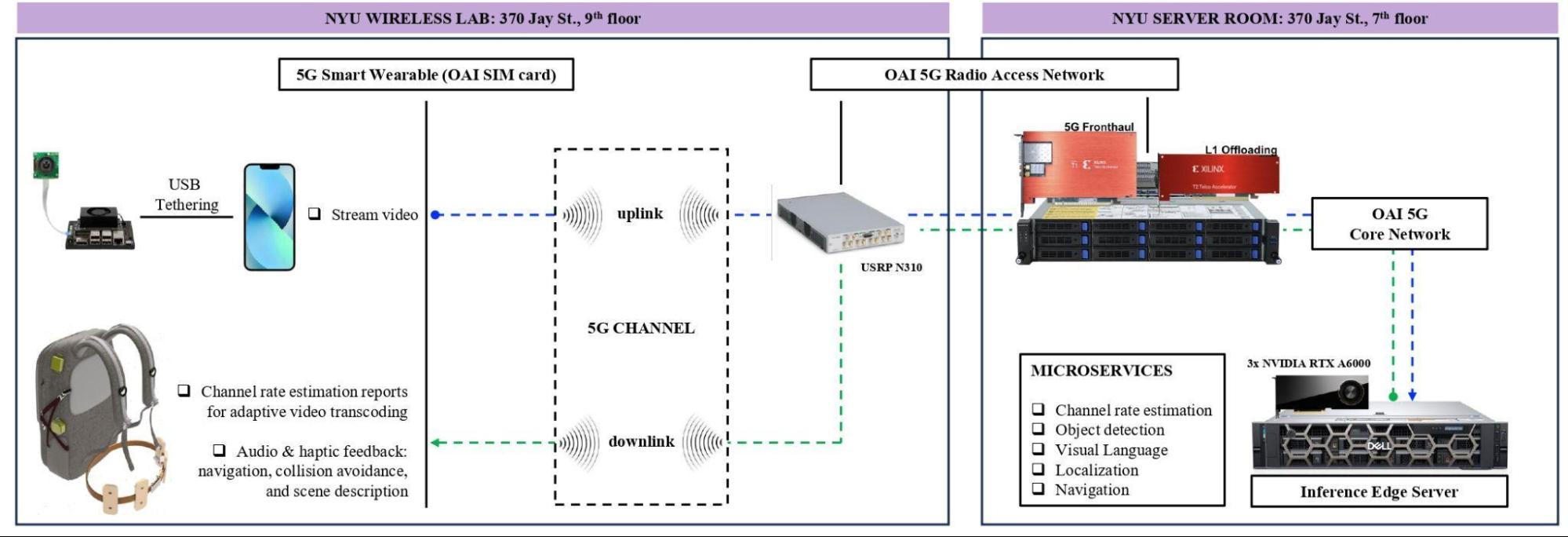
This project seeks to augment VIS4ION with wireless connectivity to access powerful AI-based microservices at the edge. These AI-based services include visual scene processing, real-time localization and navigation, and audio assistance through vision-language models and are ideally run in the cloud to access sufficient computational processing. Developing advanced wirelessly connected AI-based services presents unique challenge including the need to partition functionality between the wearable and cloud; adapt to time-varying network conditions; provide sufficient bandwidth to support high rate camera sensor data; and provide sufficiently low latency to support fast interactive services and collision avoidance. Our work includes:
- Development of a full video streaming platform to support the real-time fruition of the envisioned microservices for people with blindness and low vision. The implementation supports concurrent execution of the AI-based microservices over a pool of available GPU resources.
- Fast methods for link rate estimation and adaptation across different services.
- Evaluation in an open-source 5G testbed based on open air interface (OAI) in an indoor lab environment.
follow this research
*stay current with research in this area by completing this form

 2026 Open House
2026 Open House 2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit — November 5-7
2025 Brooklyn 6G Summit — November 5-7 Sundeep Rangan & Team Receive NTIA Award
Sundeep Rangan & Team Receive NTIA Award